Pediatric Dentistry
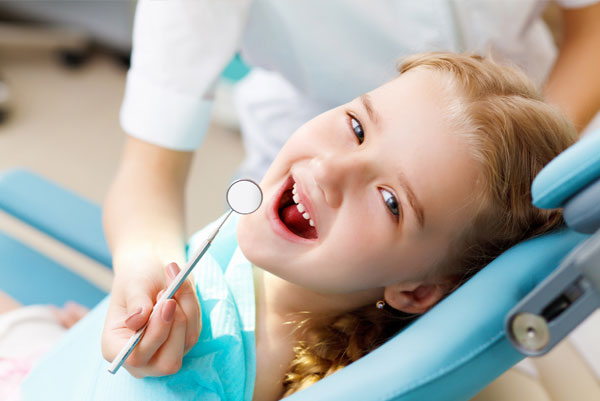

The specialist in Dental Medicine that serves children is called Pediatric Dentistry. Yet, there are dentists without the specialty can also attend children. The main success of a dentist is the empathy he creates with the child and the way he puts it at ease in consultation with accessible and appropriate conversation to the patient in the chair.
When to start?
The pediatrician initiates parent education for correct oral health as soon as babies are born with advice for correct oral hygiene. It is advisable to go to the dentist when the child already has the first deciduous teeth (milk teeth). There are pediatricians who advise to make the first consultation at age 3 when they complete the decidua dentition. If your child has a tendency to have cavities, you should see your dentist more regularly every 3 months, otherwise you should consult every 6 months.
Book now an appointment near you!
We will respond in a moment.
“There is no more beautiful landscape,
than a child’s smile.”

Frequently asked questions
What are the symptoms associated with eruption of the first teeth?
As a rule babies during tooth eruption become more cranky, loss of appetite, difficulty sleeping, increased salivation. They may have mild fevers and diarrhea.
How many teeth they have, and at what age do the eruptions start?
The first teeth to erupt are the lower incisors and between the 6-9 months, although some children may have variations, and the girls are earlier. The deciduous dentition has 20 teeth. The eruption of milk teeth is complete on average at 3 years.
The permanent dentition (definitive teeth) begins at age 6 with eruption of the lower molars and lower central incisors and is complete on average at 18 years old with eruption of 3rd molars (wisdom teeth). The permanent dentition is 32 teeth if the four wisdom teeth erupt.
In what situations should I be more attentive to my child's dentition?
1. Rampant cavities: Frequent and very extensive when good oral hygiene is not practiced and if the child consumes sugars (chocolates, wafers) for short periods of time. Before bedtime and after drinking the milk should always brush your teeth and never go to bed after eating without brushing your teeth. Cavities are most commonly found in the molars (back teeth). Attention to mothers who have a habit of giving chocolate milk or sugars in the bottle to numb the children (bottle caries).
2. Definitive eruption of teeth without “milk” teeth: Very often, the lower central incisor appears behind the “milk” tooth.
3. Language Brake: It may happen that the tongue has movements “stuck” because it has a short or close to the tip of the tongue (Anquiloglossia), which makes speech, swallowing and breastfeeding difficult.
4. Lip Brake: It can be very fibrous and low insertion causing a diastema (space) between the upper central incisors. It is indicated for surgery (Frenetomy) around 9-10 years when the canines erupt.
5. Injuries: Frequent dropping of children, especially those who start walking, is often associated with dental trauma. If there is partial or total fracture of the tooth it should be possible to keep the dental fragment. If there is a complete avulsion (loss) of the tooth, you should store it in saline, saliva or milk, if it is possible to put the tooth in its initial position until you reach your dentist. The change in color of the tooth to a yellowish color is another of the symptoms that can happen due to necrosis of the nerve and should watch over the tooth until eruption of the definitive.
If my child has tooth decay, should I treat or remove?
The dental eruption has its own chronology that must be respected. Early extraction of temporary teeth can lead to delays in eruption of definitive teeth or even prevent eruption if space is not maintained. Whenever possible, the temporary tooth should be rehabilitated in order to maintain masticatory function and aesthetics and, above all, avoid painful situations for the child.
What are Fissure Sealants?
Fissure sealants is a “varnish” (resin) that is placed in the fissures of the definitive molars to prevent the formation of caries. They are usually placed only in the definitive molars (first and second molars) and premolars after their complete eruption at about 6-7 years and 11-14 years respectively.
It is a preventive measure and should not be generalized for all children, only for those who have an incidence of high caries.
Should I give fluoride to my son?
The theme of Fluor in children is controversial because of disparity of opinion. Nowadays it is chosen only by the fluoride present in the toothpastes, on the one hand because the child always swallows part of the paste and on the other hand because it contains enough fluorine. In some cases the topical application of fluoride in trays can be done in the office.
The drops and tablets previously recommended by the Oral Health Program should only be implemented in schools when there is a high risk for caries and for children over 3 years of age.
At what age should we start brushing children?
Newborn up to 6 months:
Prior to eruption of the 1st tooth, it should be performed with a sterile gauze soaked in saline solution or water and especially after breastfeeding.
6 months – 3 years:
It should be done by a soft toothbrush with a drop of fluoride toothpaste, preferably with a pleasant taste for children (equivalent to the fingernail of the 5th finger of the hand).
From the age of 24 months the children already have a certain autonomy and we should motivate them to brush the teeth by exemplifying and supervising. But parents are always responsible for brushing.
3-6 years:
Children should brush their teeth alone but parents should always rectify brushing. You should never do it alone.
From 6 years old:
Children with manual dexterity should wash their teeth alone and always 2xs per day, especially before bedtime, but parents are always responsible for supervision and confirmation of proper brushing.
Is it advisable to use dental floss and elixir in children?
If the child already has manual dexterity and sufficient autonomy, he / she can pass the wire / dental tape. It complements tooth brushing and prevents cavities forming between the teeth.
At what age should I remove the pacifier from my child?
The pacifier is advised to remove between the 1st and 2nd year, especially in children who already have the pacifier-shaped palate and the teeth projected forward.
The use the pacifier until later ages conditions the dental and skeletal development being able to be responsible for bone malformations and joint problems. Attention to the pacifier not being replaced by the finger, digital sucking (sucking the finger) is more harmful than the pacifier.
Should parents accompany their children or wait in the waiting room?
Above all, it depends on the child and relationship with the parents. As a rule up to the age of three, parents should accompany children, especially in cases of accidents. But it has been proven that children work better in the absence of their parents. Many times it is parents who transmit anxiety to their children and promise gifts in exchange for good behavior to lead to child collaboration. In these situations, the child ends up not collaborating because he perceives that he dominates the situation.
In extreme cases of lack of collaboration, it may be necessary to resort to conscious sedation or general anesthesia that should be performed only in a hospital setting.
What are the situations that can lead to tooth color change?
Dental caries, dental trauma (falls), poor brushing, pigmentation due to eating habits or bacterial infection, enamel and dentine malformations (whitish spots) are one of the many factors responsible for color change.
Did you know that...
In the past parents used to put honey in the pacifier or bottle for the children to fall asleep and were responsible for the formation of cavities (bottle caries).
The introduction of semi-solid and solid foods into the baby’s diet is responsible for correct bone and dental development.
There are babies that can be born with teeth, birth teeth.
Prolonged breastfeeding (from 2 years onwards) can lead to excessive bone development of the mandible (Prognaths).
You should brush your child’s teeth at least 2 times a day (after breakfast and even before bed after supper).


